[ad_1]
It’s probably fair to say that anyone reading these words understands conceptually how physically connected devices communicate with each other. In the most basic configuration, one wire establishes a common ground as a shared reference point and then the “signal” is sent over a second wire. But what actually is a signal, how do the devices stay synchronized, and what happens when a dodgy link causes some data to go missing?
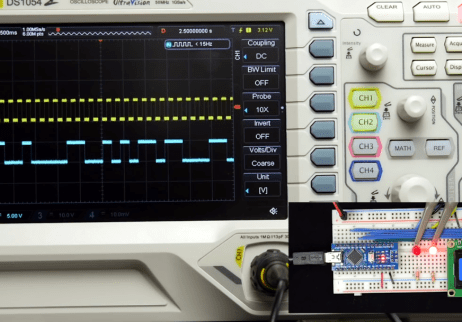 All of these questions, and more, are addressed by [Ben Eater] in his fascinating series on data transmission. He takes a very low-level approach to explaining the basics of communication, starting with the concept of non-return-to-zero encoding and working his way to a shared clock signal to make sure all of the devices in the network are in step. Most of us are familiar with the data and clock wires used in serial communications protocols like I2C, but rarely do you get to see such a clear and detailed explanation of how it all works.
All of these questions, and more, are addressed by [Ben Eater] in his fascinating series on data transmission. He takes a very low-level approach to explaining the basics of communication, starting with the concept of non-return-to-zero encoding and working his way to a shared clock signal to make sure all of the devices in the network are in step. Most of us are familiar with the data and clock wires used in serial communications protocols like I2C, but rarely do you get to see such a clear and detailed explanation of how it all works.
He demonstrates the challenge of getting two independent devices to communicate, trying in vain to adjust the delays on the receiving and transmitting Arduinos to try to establish a reliable link at a leisurely five bits per second. But even at this digital snail’s pace, errors pop up within a few seconds. [Ben] goes on to show that the oscillators used in consumer electronics simply aren’t consistent enough between devices to stay synchronized for more than a few hundred bits. Until atomic clocks come standard on the Arduino, it’s just not an option.
[Ben] then explains the concept of a dedicated clock signal, and how it can be used to make sure the devices are in sync even if their local clocks drift around. As he shows, as long as the data signal and the clock signal are hitting at the same time, the actual timing doesn’t matter much. Even within the confines of this basic demo, some drift in the clock signal is observed, but it has no detrimental effect on communication.
In the next part of the series, [Ben] will tackle error correction techniques. Until then, you might want to check out the fantastic piece [Elliot Williams] put together on I2C.
[Thanks to George Graves for the tip.]
[ad_2]
Source link